Data that was once securely encrypted can now be broken by parallel processing power. SSL and Virtual Private Networks can’t always protect messages as they travel across intermediary pathways. So, that where virtual Dispersive networking comes in.
VDN takes a page out of the traditional military radio spread spectrum security approaches. Whereas radios rotate through the frequencies randomly or splits communications and splits each communication traffic into the multiple streams. So, that only the one receiving radio can reassemble them properly. With Dispersive, however the internet (or any network) is now the underlying the communications platform.
VDN splits the message into some multiple parts, and it will encrypt each component separately and routes them over many servers, computers and even mobile phones. Traditional bottlenecks can be completely avoided.
The data also ‘roll’ dynamically to optimum paths — both randomizing the paths the messages take while simultaneously taking into the account congestion or other network issues
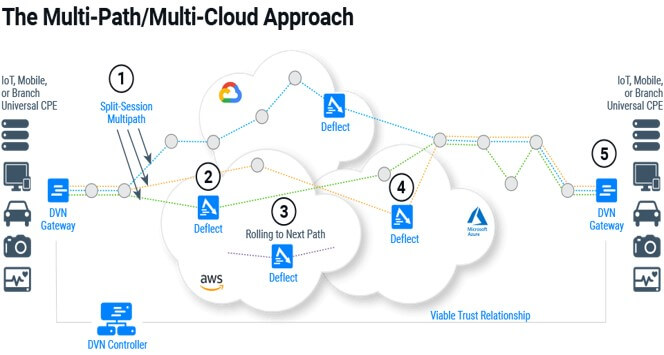
Hackers are left scrambling to find out data parts as they go through like data centers, Cloud, Internet and so on. To prevent cyber criminals from attacking the weak point of the technology — the place “where the two endpoints must connect to a switch to initiate their secure communications” — Dispersive has a hidden switch that also leverages the VDN. This makes the switch very hard to find.
Why Virtual Dispersive Networking:
- Unprecedented Security: Dispersing the data over multiple paths eliminates the Man-in-the Middle threat. Hackers can only obtain small pieces of the original file on any given pathway, rendering any data obtained meaningless.
- Network Resilience: Reliability and Resilience go hand in hand. When a connection is lost on any one of several open pathways, data packets are then rerouted to an already existing path, or an additional path is established — resulting in negligible network downtime.
- Speed / Performance: VDN traffic is dispersed over multiple independent paths using unique methods, increasing available bandwidth and optimizing data flows on individual pathways. Hence, speed and performance are increased.
VDN In-Depth
A method for network communications from a first device to a second device includes communicating data from the first device to the second device by spawning a first virtual machine for a first network connection that virtualizes network capabilities of the electronic device, and using the virtualized network capabilities of the first virtual machine, transmitting a plurality of packets for communication to a first network address and port combination associated with the second device.
The method further includes repeatedly changing to a respective another network address and port combination by repeatedly spawning a respective another virtual machine for a respective another network connection that virtualizes network capabilities of the electronic device, and using the virtualized network capabilities of the spawned respective another virtual machine, transmitting a plurality of packets for communication to the respective another network address and port combination associated with the second device.